Share the post "The History of Sailing and its Role in Society"
Sailing has been the heartbeat of exploration for thousands of years. It moved armies, built empires, and connected cultures in ways that shaped the world we know today.
From the first reed boats drifting down the Nile to the high-tech yachts racing in the Olympics, the evolution of sailing is nothing short of extraordinary. Today, we don’t just sail to trade or conquer, we sail to feel free.
Ready to dive into history? Let’s cast off and look back at where it all began. Experience a part of sailing history with a boat rental at Click&Boat!
Sailing in Ancient Civilisations (4000 BCE to 400s CE)
The story starts in the cradles of civilisation: the Mediterranean, the Persian Gulf, and the South China Sea.

Reed Boats
The Ancient Egyptians used the earliest recorded sailboats in the form of reed boats. These boats were used from 4000 BCE onwards for fishing, transportation, and trade along the Nile River. Constructed from bundles of papyrus reeds, reed boats featured a single square sail. Over time, they became larger and more complex. The use of sailboats revolutionised trade and transport. As a result, the Ancient Egyptians’ trade networks expanded beyond the Nile River into the Red Sea and the Mediterranean.
Galleys
The Phoenicians developed galleys, which were propelled by oars and sails. The Ancient Greeks, Romans, and Phoenicians used galleys from 1500 BCE to 500 CE for trade and warfare. The ships were long and narrow and designed for maritime battles. The Greeks later developed Triremes which were manned by up to 200 crew members. Triremes had more speed and mobility than Galleys with three oar banks on each side. In addition, they were armed with various weapons, which was useful in ancient naval warfare. Hence, triremes played a crucial role in the victories of Athens and Sparta in the Peloponnesian War.
The history of sailing in the Middle Ages (400s to 1400s)
The Middle Ages conceived inventions that changed the course of sailing history. The Chinese invented the compass, transforming maritime navigation. A compass allowed sailors to determine their direction accurately using the Earth’s magnetic field without using stars or landmarks. The Greeks developed the Astrolabe, a sophisticated instrument allowing sailors to determine their latitude by measuring the altitude of celestial bodies.
Junk Ships

During the Han dynasty, the Chinese designed junks ships. They used junks for trade and exploration in the South China Sea, sailing as far as East Africa, the Middle East, and Southeast Asia. They featured multiple masts and square sails, allowing them to catch the wind from different angles. Junk ships could sail long distances across open seas, even in adverse weather conditions. Their advanced rigging and sail systems allowed them to sail upwind, a prominent advantage over other sailing vessels of the time.
Longships
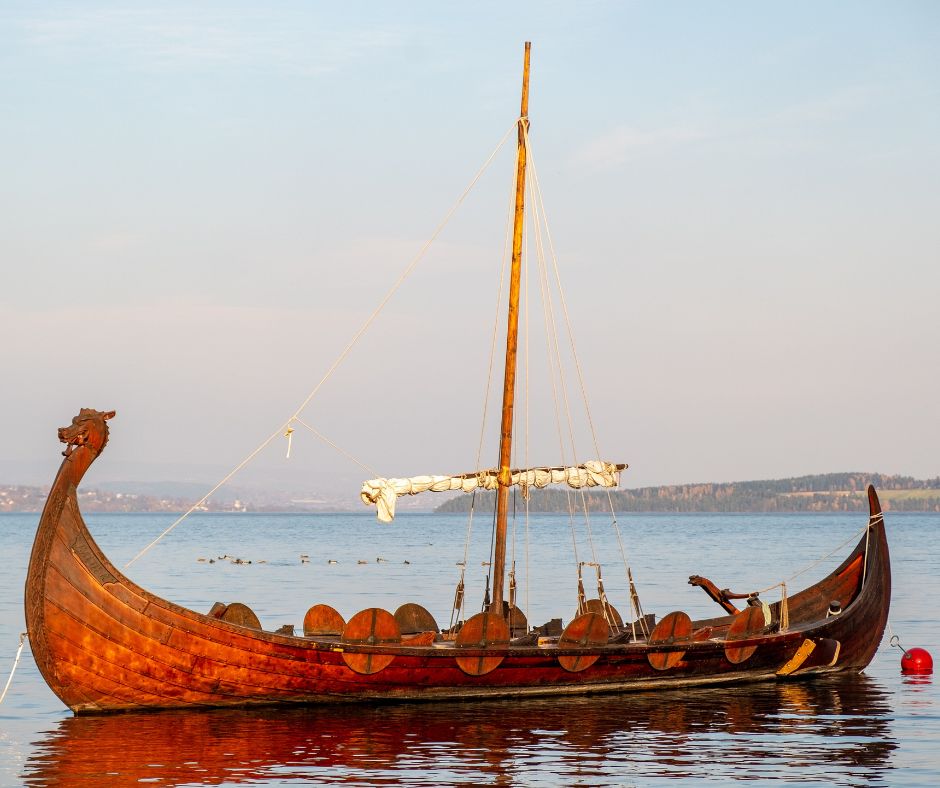

The Vikings used longships for trade, exploration, and warfare throughout the Viking age between the 8th and 11th centuries. The longship’s design allowed it to travel at high speeds, ideal for surprise attacks and raids along the coasts of Europe. The image above is a smaller replica of a longship. While they look simple, longships transported the Vikings across the North Atlantic to Iceland, Greenland, and even North America!
The Age of Sail (1400s to 1800s)
The Age of Sail significantly impacted the development of maritime trade and exploration. Historians refer to this time as the golden age of sailing history. This age saw European explorers sail around the world seeking new lands and resources. Lateen sails were popularised during this time. These triangular sails were more efficient than the traditional square sails so boats could catch wind from different directions. Americans invented the sextant in the 18th century. It allowed sailors to determine their latitude and longitude by measuring the angle between the horizon and a celestial body.
Caravels
During the Age of Exploration, starting in the 15th century, European sailors, including Christopher Columbus, used caravels to explore new trade routes and establish colonies in the Americas. Caravels were perfect for long-distance maritime exploration. The boat’s lateen sails allowed them to sail against the wind and navigate coastal areas and narrow straits. Additionally, caravels were often armed with cannons and other weapons, making them effective in trade and warfare.
Galleons
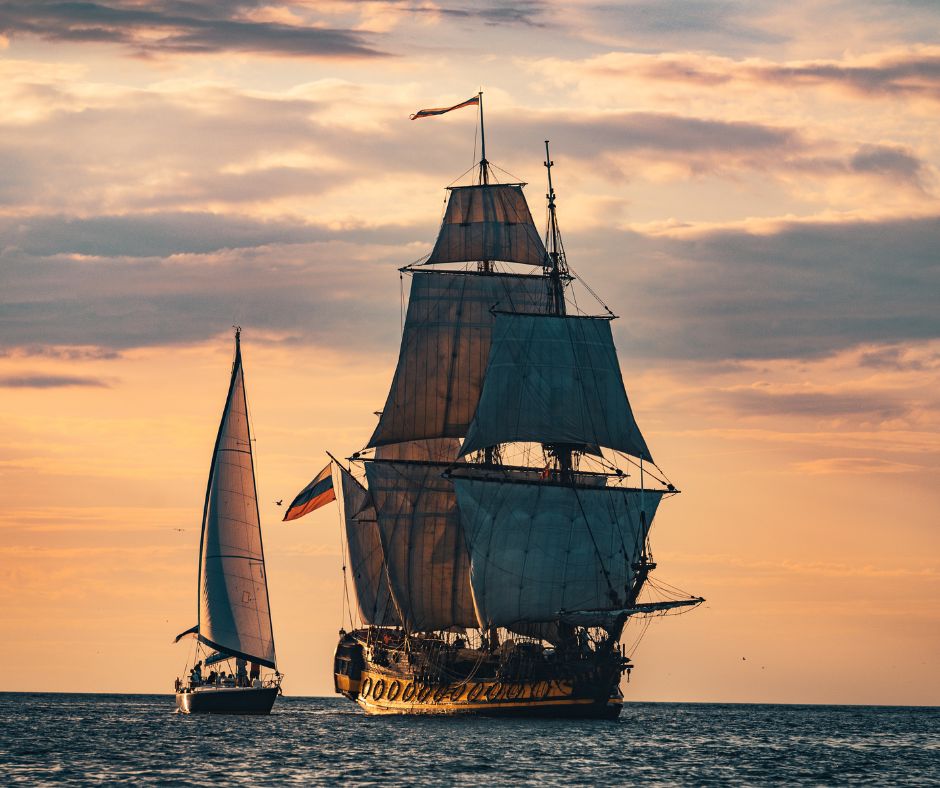

European powers such as Spain and Portugal developed galleons, large, heavily armed sailing ships, in the 16th century. They carried large amounts of cargo, including precious metals and spices. Galleons were also crucial in establishing trading networks and colonies in the Americas, Asia, and Africa. Their design innovations made them more effective than previous sailing ships. They were equipped with multiple decks and a high freeboard for ample storage. They also had a rounded hull shape for increased speed and mobility. Galleons played a significant role in the Age of Sail and are an iconic symbol of maritime history and exploration. These are the boats used in the Pirates of the Caribbean movies! Curious to find more movies featuring sailing? Check out this blog!
Sailing: the modern era (the 1800s to the present)
While sailing has played a central role in human civilisation for thousands of years, its importance has diminished somewhat in the modern era. The industrial revolution changed the course of sailing history with the rise of steamboats. Air travel also transformed global travel, making it faster and more efficient. However, sailing remains a popular pastime and sport, with millions worldwide enjoying recreational sailing, competitive racing, and cruising.
The history of sailing as a sport
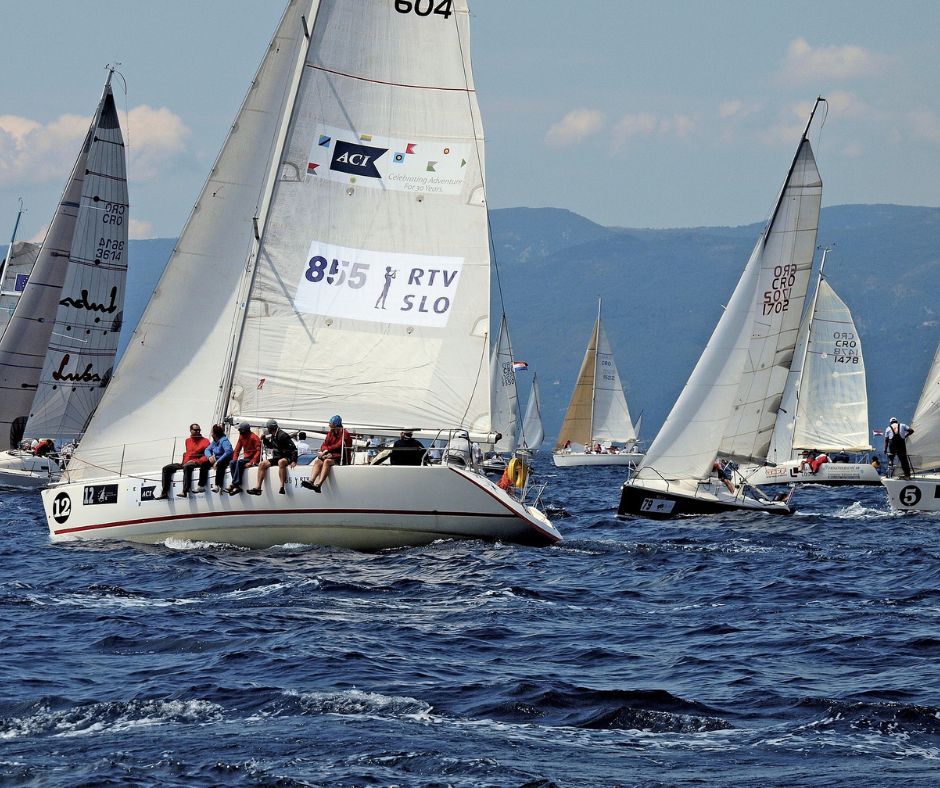

Sailing for fun really took shape in 17th-century England. King Charles II, a passionate sailor himself, championed yachting after the Restoration in 1660. His royal support helped formalise racing and led to the founding of the Cork Water Club in 1720, the world’s first yacht club.
The real turning point? The launch of the America’s Cup in 1851. This elevated sailing to an international spectacle. As technology evolved, boats became lighter and faster, paving the way for the incredible races and Olympic events we watch today.
Sailing is for Everyone
Today, sailing is more accessible than ever. You don’t need to be an explorer or an aristocrat to feel the wind in your hair. Modern catamarans and yachts are designed for comfort and ease, welcoming sailors of all backgrounds.
At Click&Boat, we believe the sea belongs to everyone. Whether you’re an expert skipper or just looking for a relaxing day on the water, we make it easy to rent a boat and write your own chapter in sailing history.
FAQ
When was sailing first invented?
It dates back to around 4000 BCE. Ancient civilisations, like the Egyptians, used reed boats with simple square sails to navigate the Nile.
Which civilisation impacted early sailing the most?
The Phoenicians, Greeks, and Egyptians were key players. They developed advanced ship designs and navigation techniques that opened up trade across the Mediterranean.
How did sailing change the world?
It allowed humanity to explore new continents, build global trade networks, and share ideas across oceans, especially during the Age of Sail (15th–18th centuries).
What were the biggest sailing inventions?
The compass, astrolabe, and sextant were game-changers. They allowed sailors to navigate accurately using the stars and the Earth’s magnetic field.
Why is sailing still popular today?
It’s the ultimate escape. While we don’t need sails for trade anymore, sailing connects us to nature, history, and the thrill of adventure.